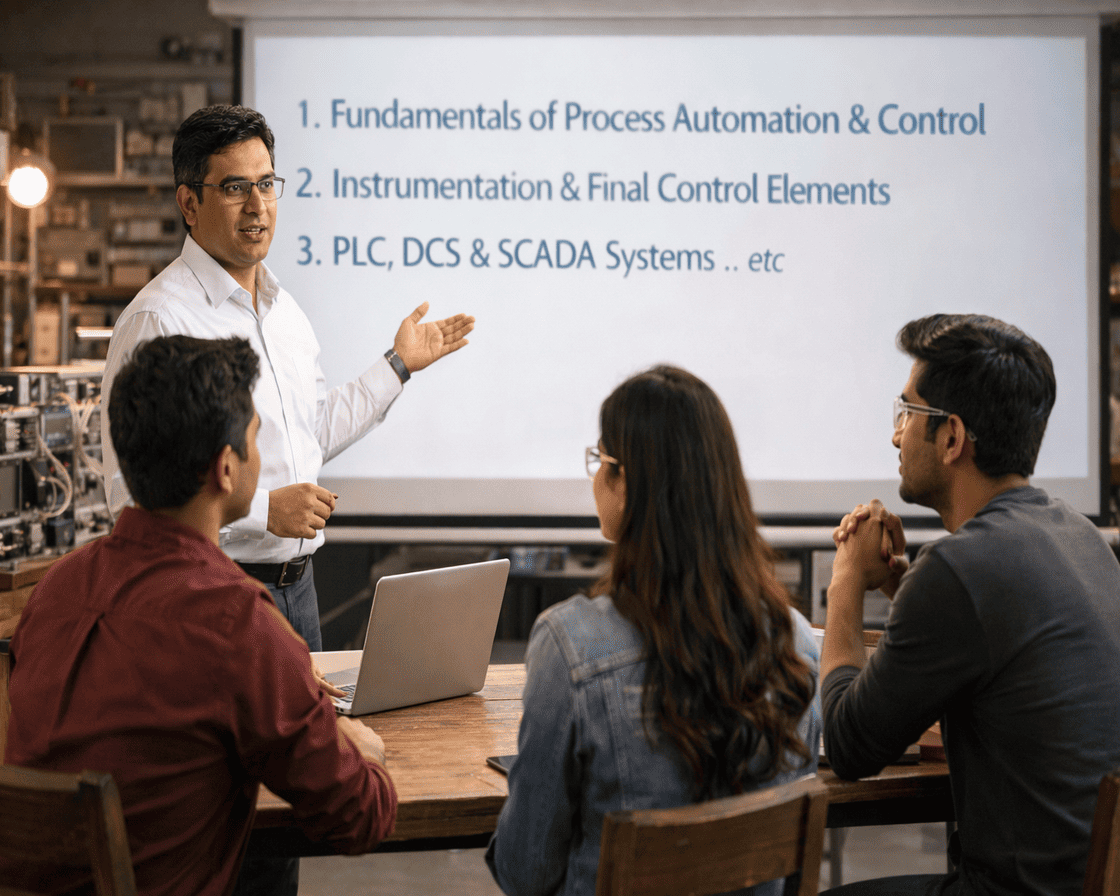
Welcome to Robotriq — a professional institute focused on industrial automation training and practical skill development. We are committed to helping engineers, technicians, and working professionals gain job-ready automation skills through hands-on, industry-focused learning.